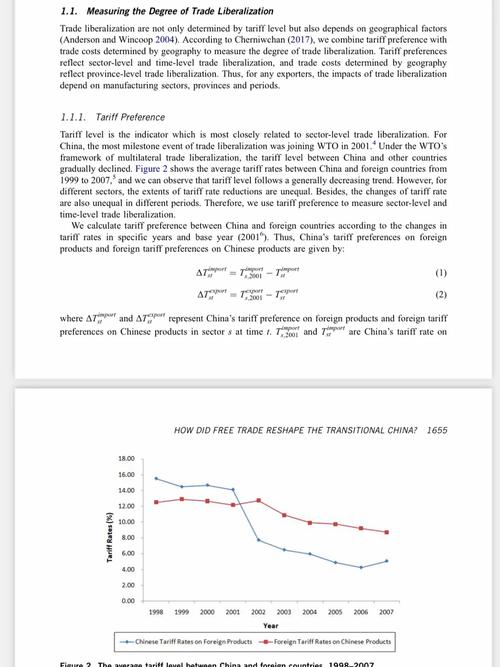
How is Sand Produced?
Sand, a seemingly simple and ubiquitous material, plays a crucial role in various industries and everyday life. But have you ever wondered how sand is produced? This article delves into the fascinating process of sand production, exploring its sources, types, and applications.
Where Does Sand Come From?
The primary source of sand is the weathering and erosion of rocks. Over time, rocks are broken down into smaller particles by natural processes such as wind, water, and ice. These particles are then transported and deposited in various environments, including rivers, lakes, beaches, and deserts. The most common rock types that contribute to sand production are quartz, feldspar, and limestone.
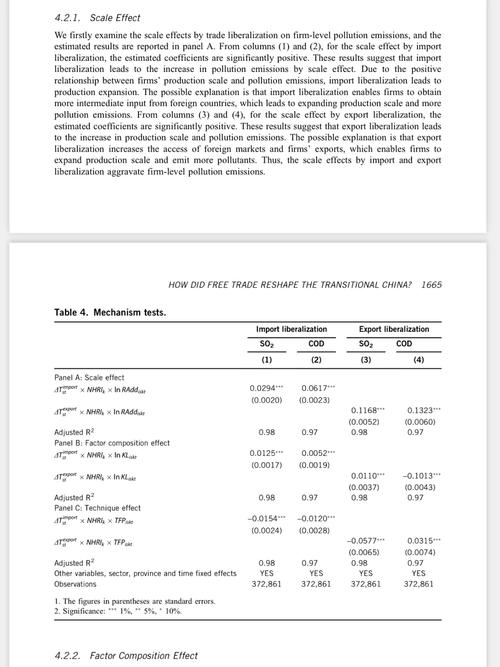
Types of Sand
Sand can be categorized into different types based on its composition, grain size, and origin. Here are some of the most common types of sand:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Quartz Sand | Composed primarily of quartz, this type of sand is hard, durable, and resistant to chemicals. It is widely used in glass manufacturing, foundry, and construction industries. |
| Feldspar Sand | Rich in feldspar minerals, this sand is used in the production of ceramics, glass, and as a flux in steelmaking. |
| Limestone Sand | Derived from limestone, this sand is used in the construction industry for concrete and asphalt production. |
| Beach Sand | Composed of a mix of minerals, beach sand is used for landscaping, sandblasting, and as a filtration medium in water treatment plants. |
How is Sand Extracted?
Sand extraction involves mining the sand from its natural source. There are two primary methods of sand extraction: open-pit mining and dredging.
Open-pit Mining: This method is used when the sand deposit is located above the ground. Large machinery, such as excavators and loaders, are used to remove the sand from the pit. The extracted sand is then transported to a processing plant for further treatment.
Dredging: When the sand deposit is underwater, dredging is the preferred method. Dredging involves using a dredge, which is a machine that scoops up sand from the bottom of a body of water. The sand is then pumped to a processing plant for treatment.
Processing Sand
Once the sand is extracted, it undergoes a series of processing steps to remove impurities and achieve the desired quality. The primary processing methods include:
- Screening: This process separates the sand into different sizes using screens. The sand is passed through the screens, and the particles that fit through the openings are collected.
- Washing: To remove any remaining impurities, the sand is washed with water. The water helps to dislodge and wash away the unwanted materials.
- Drying: After washing, the sand is dried to remove excess moisture. This can be done using natural sunlight, wind, or mechanical dryers.
Applications of Sand
Sand has a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the most common uses include:
- Construction: Sand is a key ingredient in concrete, asphalt, and mortar. It provides strength and stability to these materials.
- Manufacturing: Sand is used in the production of glass, ceramics, and steel. It acts as a flux, helping to remove impurities from the molten materials.
- Landscaping: Beach sand is used for landscaping purposes, such as creating sandboxes, playgrounds, and artificial beaches.
- Water Filtration: Sand is used in water treatment plants to filter out impurities and improve water quality.
In conclusion, sand is produced through the weathering and erosion of rocks, and it undergoes various processing steps to achieve the desired quality. Its diverse applications make it an essential material in numerous industries and everyday life.
