Sand Battery Disadvantages
As the world increasingly seeks sustainable and renewable energy solutions, the sand battery has emerged as a promising candidate. However, like any technology, it comes with its own set of disadvantages. In this article, we will delve into the various drawbacks associated with sand batteries, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of their limitations.
Energy Density
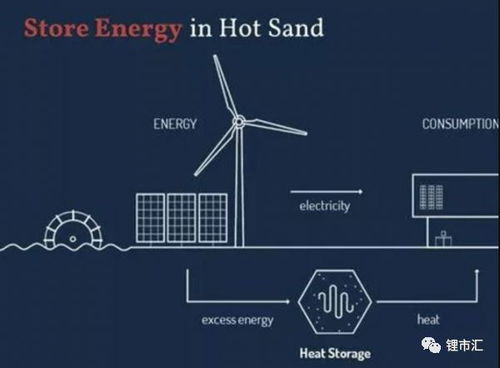
One of the most significant disadvantages of sand batteries is their relatively low energy density. Energy density refers to the amount of energy stored in a given volume or mass of a battery. Sand batteries have an energy density that is much lower compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. This means that sand batteries require a larger physical size to store the same amount of energy, which can be impractical for portable devices or vehicles.
| Energy Density Comparison | Sand Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density (Wh/kg) | 50-100 | 150-250 |
Charging Time

Another drawback of sand batteries is their relatively slow charging time. While lithium-ion batteries can be charged in a matter of hours, sand batteries can take several days to fully charge. This slow charging time can be a significant inconvenience for users who require quick access to energy, such as those using portable devices or electric vehicles.
Cost

The cost of sand batteries is another significant disadvantage. Currently, the production cost of sand batteries is higher compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. This is primarily due to the complex manufacturing process and the high cost of raw materials. As a result, sand batteries may not be as cost-effective for widespread adoption, especially in the consumer electronics market.
Environmental Impact
While sand batteries are considered a more sustainable alternative to traditional batteries, they still have an environmental impact. The mining and processing of raw materials, such as sand, can have negative effects on the environment, including habitat destruction and water pollution. Additionally, the disposal of sand batteries at the end of their life cycle can pose challenges, as they contain potentially harmful materials.
Lifetime and Performance Degradation
Like all batteries, sand batteries experience a decrease in performance over time. This degradation is primarily due to the gradual loss of active material within the battery, which reduces its overall energy storage capacity. While sand batteries have a longer lifespan compared to some other battery technologies, they still face the challenge of maintaining consistent performance throughout their use.
Thermal Management
Thermal management is another critical concern for sand batteries. As batteries charge and discharge, they generate heat, which can lead to performance degradation and even safety risks. Effective thermal management systems are required to dissipate this heat and maintain optimal operating conditions. However, implementing such systems can add complexity and cost to the overall design of sand batteries.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while sand batteries offer a promising alternative to traditional battery technologies, they come with several disadvantages. These include low energy density, slow charging times, high production costs, environmental impact, performance degradation, and thermal management challenges. As research and development continue to advance, it is essential to address these limitations to ensure the widespread adoption of sand batteries in various applications.
