Sand, Silt, Clay: A Detailed Exploration of Particle Size
Understanding the particle size distribution of soil is crucial in various fields, from agriculture to environmental science. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of sand, silt, and clay particles, exploring their characteristics, uses, and significance in different contexts.
What is Particle Size?
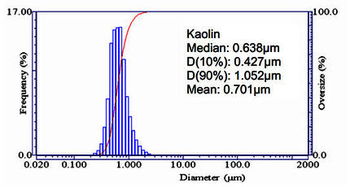
Particle size refers to the diameter of individual soil particles. It plays a vital role in determining the soil’s texture, structure, and its ability to retain water and nutrients. Particle sizes are typically categorized into three main groups: sand, silt, and clay.
Sand
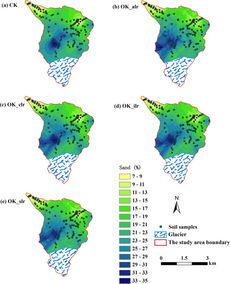
Sand particles are the largest of the three, with diameters ranging from 0.05 to 2.0 millimeters. They are composed of weathered rock fragments and are easily visible to the naked eye. Sand particles are rough and angular, which contributes to their ability to drain water quickly. This characteristic makes sand an excellent material for construction and landscaping projects.
Table 1: Sand Particle Size Distribution
| Particle Size Range (mm) | Percentage |
|---|---|
| 0.05 – 0.2 | 0-10% |
| 0.2 – 0.5 | 10-30% |
| 0.5 – 1.0 | 30-50% |
| 1.0 – 2.0 | 50-100% |
Silt
Silt particles are smaller than sand, with diameters ranging from 0.002 to 0.05 millimeters. They are composed of finely weathered rock fragments and are often difficult to see without magnification. Silt particles are smooth and rounded, which allows them to retain water and nutrients more effectively than sand. This characteristic makes silt an ideal soil for growing crops and supporting plant life.
Table 2: Silt Particle Size Distribution
| Particle Size Range (mm) | Percentage |
|---|---|
| 0.002 – 0.0025 | 0-10% |
| 0.0025 – 0.005 | 10-30% |
| 0.005 – 0.01 | 30-50% |
| 0.01 – 0.05 | 50-100% |
Clay
Clay particles are the smallest of the three, with diameters ranging from 0.0002 to 0.002 millimeters. They are composed of extremely fine particles and are almost invisible to the naked eye. Clay particles are extremely smooth and have a high surface area, which allows them to retain water and nutrients more effectively than silt or sand. However, clay soils can become compacted and poorly drained, which can be a challenge for agriculture and construction.
Table 3: Clay Particle Size Distribution
| Particle Size Range (mm) | Percentage |
|---|---|
| 0.0002 – 0.0005 | 0-10% |
| 0.0005 – 0.001 | 10-30% |
| 0.001 – 0.002 | 30-50% |
| 0.002 – 0.0025 | 50-100% |
