Silt and Sand Fraction: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the composition of soil is crucial in various fields, from agriculture to environmental science. One of the key components that define soil texture is the silt and sand fraction. This article delves into the details of silt and sand fractions, their characteristics, and their significance in soil science.
What are Silt and Sand Fractions?
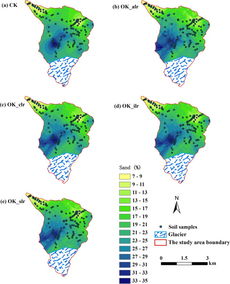
Silt and sand are two of the primary components of soil, along with clay. These fractions are classified based on their particle sizes. Silt particles range in size from 0.002 to 0.05 millimeters, while sand particles are larger, ranging from 0.05 to 2 millimeters. The presence of these fractions in soil affects its physical, chemical, and biological properties.
Characteristics of Silt and Sand Fractions

Silt and sand fractions have distinct characteristics that influence soil behavior. Here are some key points:
-
Silt particles are smaller than sand particles but larger than clay particles. They are often smooth and round, which allows them to hold water and nutrients well.
-
Sand particles are larger and more angular, which makes them less able to retain water and nutrients. However, they provide good drainage and aeration for plant roots.
-
The proportion of silt and sand in soil can vary widely, depending on the soil’s origin and environmental conditions.
Significance of Silt and Sand Fractions in Soil Science
Silt and sand fractions play a crucial role in soil science for several reasons:
-
Water Retention and Drainage: The presence of silt and sand fractions affects soil’s water retention and drainage capabilities. Soils with a higher silt content tend to retain more water, while those with more sand are better at draining excess water.
-
Soil Structure: The size and shape of silt and sand particles influence soil structure. Well-structured soil allows for better root penetration and aeration.
-
Plant Growth: The availability of water, nutrients, and oxygen in the soil directly impacts plant growth. Silt and sand fractions contribute to the overall fertility of the soil.
Table: Comparison of Silt and Sand Fractions
| Characteristics | Silt | Sand |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | 0.002 to 0.05 mm | 0.05 to 2 mm |
| Shape | Smooth and round | Angular |
| Water Retention | Good | Poor |
| Drainage | Poor | Good |
Soil Classification Based on Silt and Sand Fractions
Soil classification systems, such as the United States Soil Taxonomy, use silt and sand fractions to categorize soils. For example, a soil with a high silt content and low sand content might be classified as a loam, while a soil with a high sand content and low silt content might be classified as a sandy loam.
Conclusion
In conclusion, silt and sand fractions are essential components of soil that influence its physical, chemical, and biological properties. Understanding the characteristics and significance of these fractions is crucial for soil management, agriculture, and environmental science. By analyzing the silt and sand fractions in a soil sample, scientists and farmers can make informed decisions about soil improvement and plant cultivation.
