What Material is Sand?
Sand, a seemingly simple and ubiquitous substance, is composed of a complex mix of materials. Understanding what material sand is made of can provide insights into its properties, uses, and environmental impact. Let’s delve into the composition of sand and explore its various aspects.
Composition of Sand
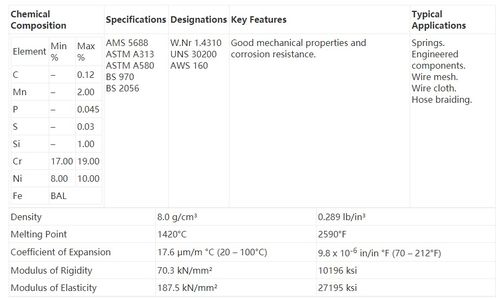
Sand is primarily made up of tiny grains of rock and mineral fragments. These grains are typically less than 2 millimeters in diameter and can vary in color, shape, and texture. The most common materials that make up sand include:
| Material | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Quartz | Most common (up to 95%) |
| Calcite | Up to 10% |
| Feldspar | Up to 5% |
| Rock fragments | Up to 5% |
| Other minerals | Up to 5% |
Quartz is the most abundant mineral in sand, accounting for up to 95% of its composition. It is a durable and hard mineral that contributes to the strength and stability of sand. Calcite, feldspar, rock fragments, and other minerals make up the remaining percentage of sand’s composition.
Formation of Sand
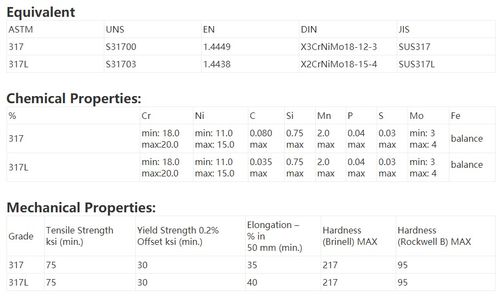
Sand is formed through the weathering and erosion of rocks over time. The process involves several stages:
-
Weathering: This is the breakdown of rocks into smaller particles due to physical, chemical, and biological processes. Physical weathering includes freeze-thaw cycles, abrasion, and root expansion. Chemical weathering involves the dissolution of minerals in water, while biological weathering is caused by the actions of plants and animals.
-
Erosion: Once the rocks are broken down into smaller particles, they are transported by wind, water, or ice. This process is known as erosion. The speed and direction of erosion depend on factors such as the type of rock, climate, and topography.
-
Deposition: The eroded particles are eventually deposited in a new location, such as a riverbed, beach, or desert. Over time, these particles accumulate and form sand deposits.
The formation of sand can take thousands to millions of years, depending on the geological processes involved.
Properties of Sand

Sand has several unique properties that make it valuable for various applications:
-
Grain size: Sand grains can range in size from fine to coarse. The grain size affects the sand’s texture, porosity, and permeability.
-
Shape: Sand grains can be angular, sub-angular, or rounded. The shape of the grains influences the sand’s packing density and stability.
-
Color: Sand can range in color from white to black, depending on the minerals present. The color can also indicate the geological origin of the sand.
-
Porosity: Sand is a porous material, meaning it can hold water and other fluids. The porosity of sand affects its ability to filter and retain water.
-
Permeability: Sand is a permeable material, allowing water and other fluids to flow through it. The permeability of sand is important for applications such as irrigation and drainage.
Applications of Sand
Sand is used in a wide range of applications, both in the construction industry and other sectors:
-
Construction: Sand is a key ingredient in concrete, mortar, and asphalt. It provides strength, stability, and workability to these materials.
-
Foundry: Sand is used in foundry operations to create molds for casting metal objects. The properties of sand, such as its grain size and shape, are crucial for the quality of the casting process.
-
Water filtration: Sand is used in water filtration systems to remove impurities and particles from water. Its porosity and permeability
